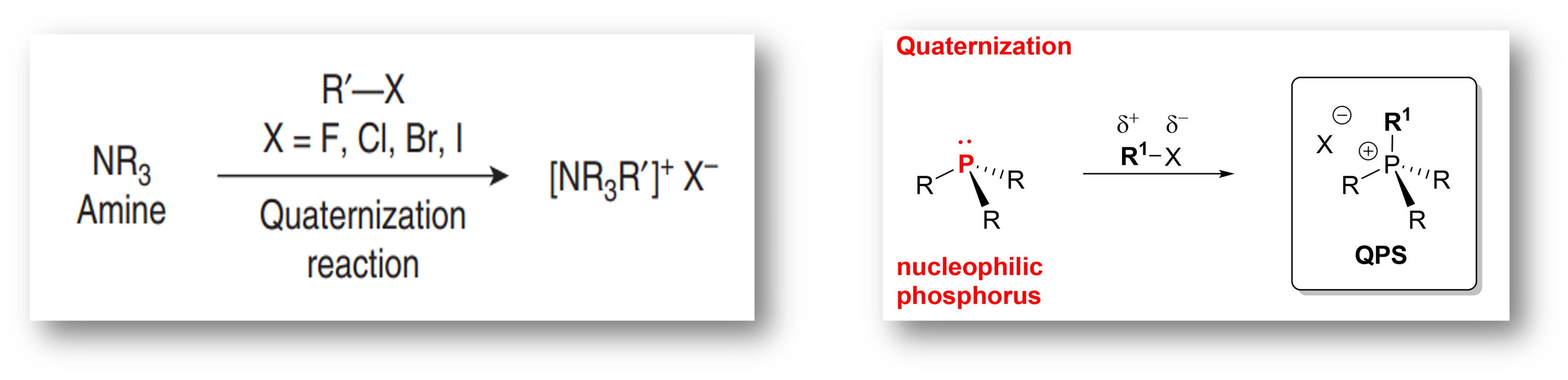
☞ Generating AIL cations through a nucleophilic substitution reaction with an alkyl halide involves quaternizing organic bases, which transforms a neutral tertiary amine or phosphine into a quaternary ammonium or phosphonium cation, respectively.
☞ The reaction can change a 3-to 4-coordinate nitrogen or phosphorus.
☞
Example
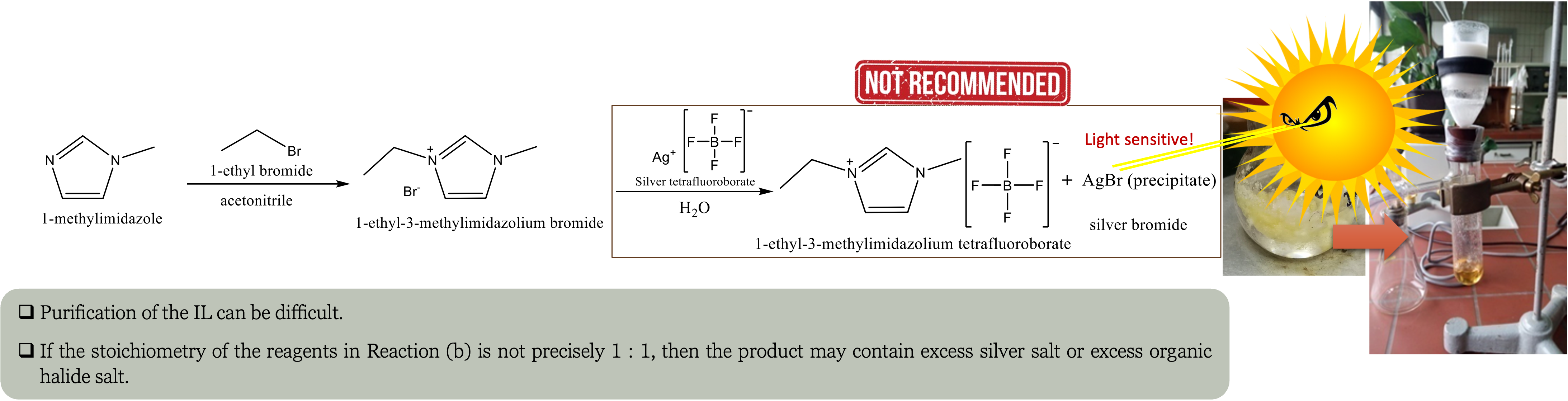
Sometimes, the counter-ion produced during quaternization may not be the intended one. In such instances, it becomes imperative to conduct an anion exchange reaction using one of the methods:
☞ METATHESIS
Replacement of the halide in a quaternary salt with a desired alternative anion.
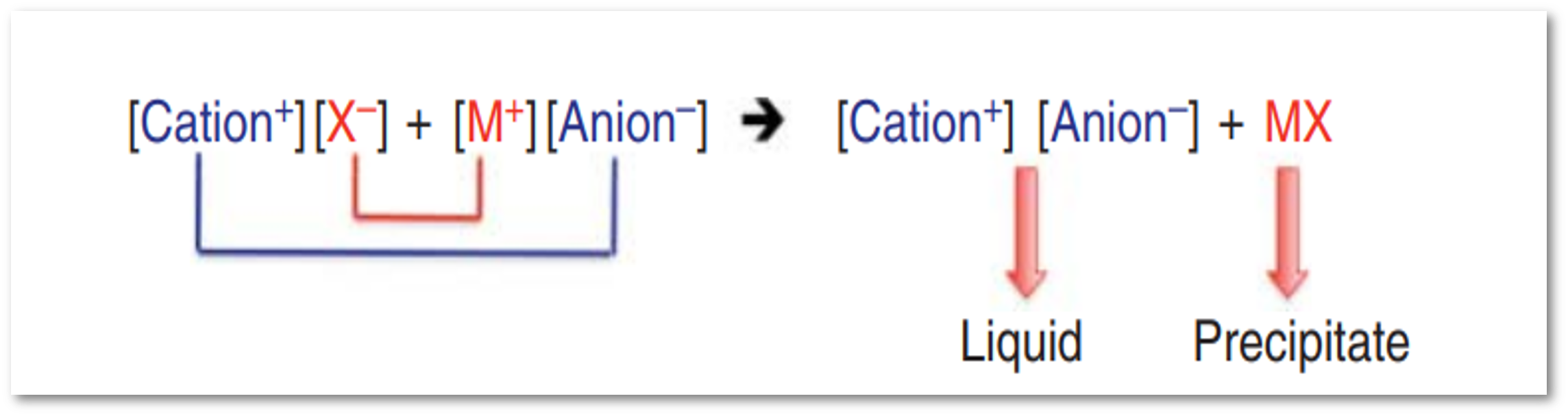
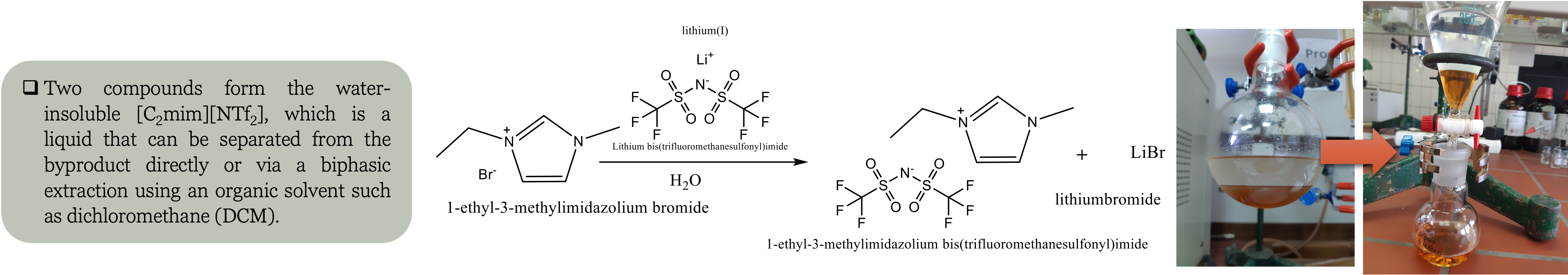
Metathesis reactions are used to produce ILs through two different pathways based on the solubility of the desired IL in water.
If the IL is hydrophilic, the reaction is conducted in water or polar solvents where water-soluble silver salts such as Ag[NO
3], Ag[BF
4], or Ag[N(CN)
2] are employed as the source of the desired anion.
The byproduct can be removed by filtration since silver halide precipitates that are insoluble in water are produced.
Example – water miscible
Example – water immiscible
☞ ION EXCHANGE
Another way to carry out metathesis is by using an ion-exchange resin. Ion exchange can be done in a chormatography column or in a lab glass.
[A][X1] + [Resin][X2] ⇄ [Resin][X1] + [A][X2]
For this exchange to take place, the affinity of the resin for [X1] must be greater than that for [X2]. If the resin has only a slightly lower affinity for [X1], then a two-step sequence involving hydroxide exchange and acid neutralization may be needed.
First, a solution of choline iodide [Ch]I in water is passed through a column filled with a hydroxide-based ion-exchange resin, such as SUPELCO® or AMBERLITE® IRA-78, or be mixed in lab glass a hydroxide-based ion-exchange resin, to produce [Ch][OH]. (
Example) Second, the solution should be checked that it does not contain halides.
If the reaction for halides is positive, the solution should be passed through a column again, or if lab glass is used, the ion-exchange resin should be replaced with a new amount. The freshly produced choline hydroxide is then reacted with excess acetic acid in water to form the desired choline acetate. Final step is
purification.