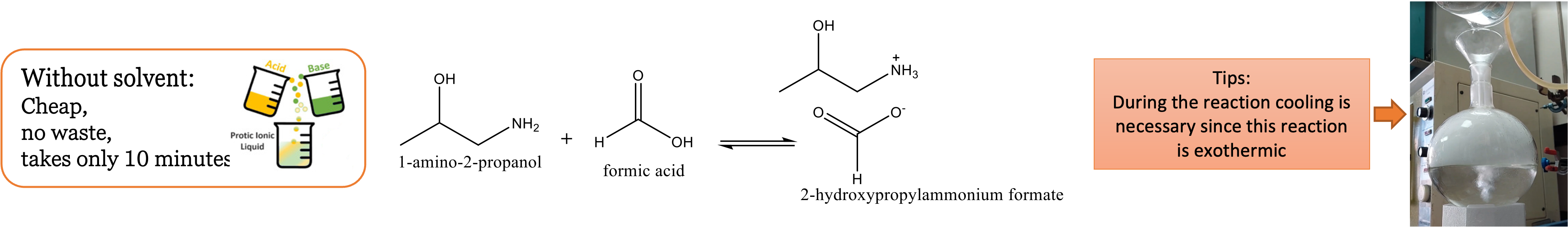
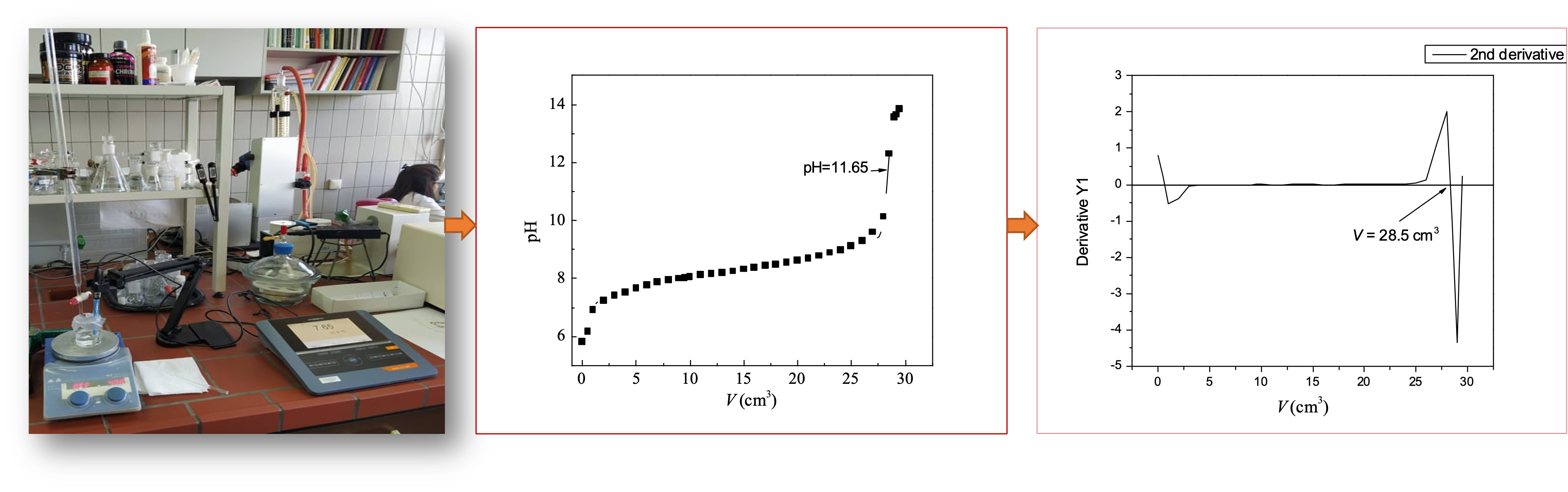
- Home
- News
- Structure
- Working groups
- WG 1: NECTAR for highly hydrolysable (HHC) and/or low-valence state (LVC) cations.
- WG 2: NECTAR for strong and/or multifunctional ligands, macromolecules, polyelectrolytes.
- WG 3: NECTAR for multicomponent solutions and complex matrices.
- WG 4: NECTAR tools, services and facilities.
- WG 5: NECTAR for the future: new trends and exploitation of results.
- Activities
- Outcomes
- Contact